ACA vs Private Insurance: Which One is Right for You?
Health insurance is a critical component of healthcare in the United States, providing financial protection against the costs of medical services. Individuals often face a choice between two primary options: health insurance plans offered through the Affordable Care Act (ACA) marketplace and private health insurance plans obtained outside of the ACA framework. Understanding the distinctions between these two types of coverage is essential for making an informed decision about health insurance. This article provides a detailed comparison of ACA and private health insurance, exploring their respective features, benefits, and drawbacks.
Table of Contents
What Is ACA Health Insurance?
The Affordable Care Act signed into law in 2010, aimed to increase access to health insurance, improve the quality of care, and reduce costs. The ACA established a framework for health insurance coverage through the creation of health insurance exchanges, where individuals can purchase plans that meet specific federal standards.
Features of ACA Health Insurance:
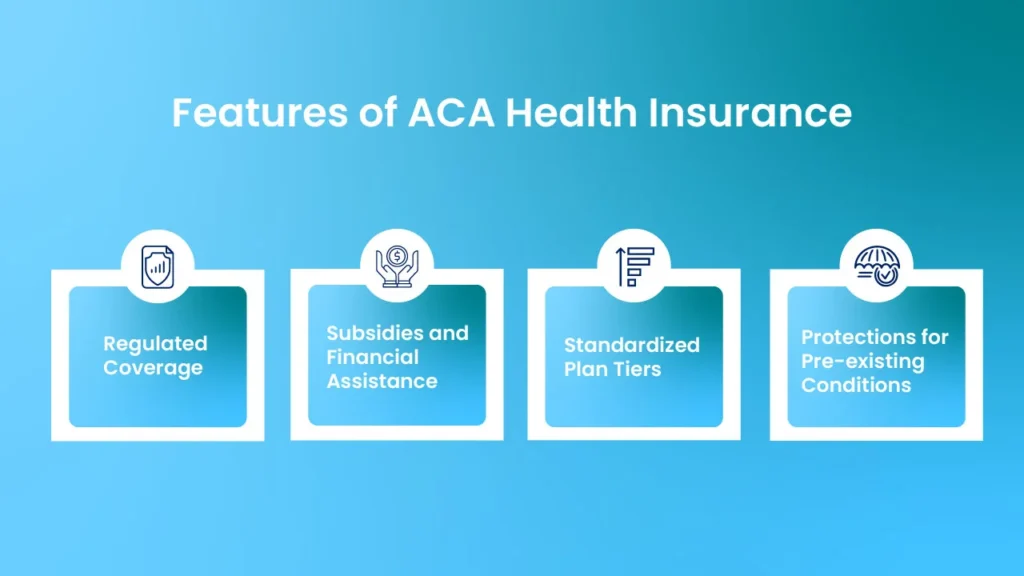
- Regulated Coverage: ACA plans must adhere to federal regulations, ensuring that they offer a set of essential health benefits, including preventive services, maternity and newborn care, mental health services, and prescription drugs.
- Subsidies and Financial Assistance: Individuals and families with incomes between 100% and 400% of the federal poverty level may qualify for premium tax credits and cost-sharing reductions, which help lower the cost of premiums and out-of-pocket expenses.
- Standardized Plan Tiers: ACA plans are categorized into metal tiers—Bronze, Silver, Gold, and Platinum—each with a defined level of coverage and cost-sharing. This standardization helps consumers compare plans based on their needs and budget.
- Protections for Pre-existing Conditions: ACA regulations prohibit insurers from denying coverage or charging higher premiums based on pre-existing conditions, ensuring that individuals with chronic or previous health issues have access to insurance.
Benefits of ACA Health Insurance:
- Comprehensive Coverage: ACA plans are designed to cover a broad range of essential health services, providing a high level of coverage for various medical needs.
- Financial Assistance: Subsidies and cost-sharing reductions make health insurance more affordable for those with qualifying incomes, reducing the financial burden of premiums and out-of-pocket costs.
- Consumer Protections: The ACA provides strong consumer protections, including coverage for pre-existing conditions and preventive services without additional cost to the insured.
Drawbacks of ACA Health Insurance:
- Potentially High Premiums: Even with subsidies, some individuals may find ACA premiums to be costly, particularly if their income is just above the subsidy threshold.
- Limited Provider Networks: Some ACA plans have narrow networks, which may restrict access to certain healthcare providers and facilities.
- Complex Enrollment Process: The ACA enrollment process can be complex, with various plans and eligibility requirements, which may be challenging for some individuals to navigate.
Private Health Insurance:
Private health insurance encompasses plans offered by private insurers outside of the ACA marketplace. These plans can be purchased directly from insurance companies, through brokers, or provided by employers.
Features of Private Health Insurance:
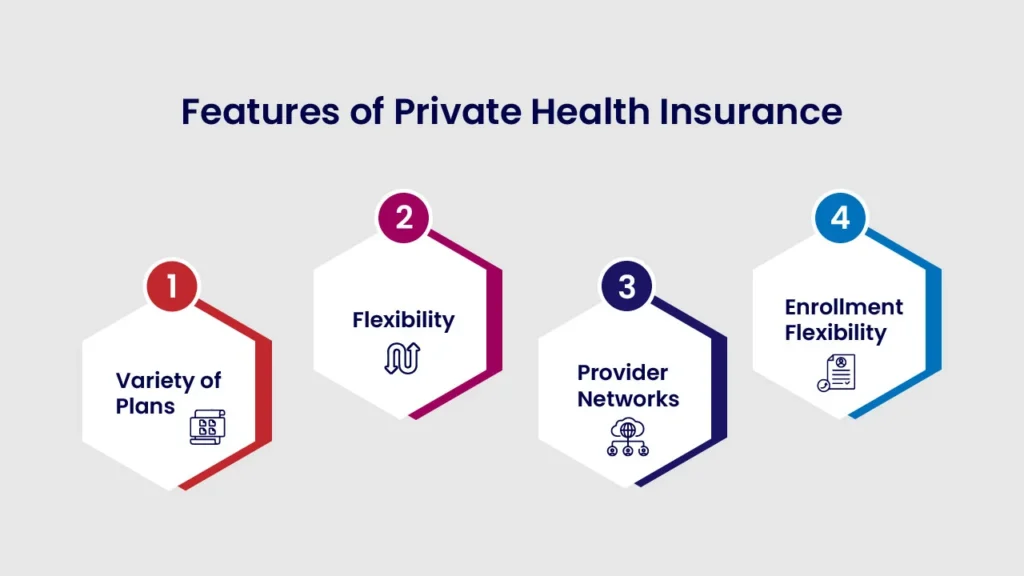
- Variety of Plans: Private health insurance offers a wide range of plan options, including different levels of coverage, deductibles, and premium costs, allowing consumers to select plans that best fit their needs.
- Flexibility: Private insurers may offer flexible plan designs, including high-deductible health plans (HDHPs), health savings accounts (HSAs), and other specialized coverage options.
- Provider Networks: Private health insurance plans may provide access to a broader network of healthcare providers and facilities, depending on the plan.
- Enrollment Flexibility: Private health insurance plans may have different enrollment periods and options, including year-round enrollment for certain plans.
Benefits of Private Health Insurance:
- Customization: Private health insurance allows for greater customization of coverage, enabling individuals to select plans that meet their specific health needs and preferences.
- Potential Cost Savings: For some individuals, particularly those who are young and healthy, private health insurance plans may offer lower premiums compared to ACA plans.
- Broader Provider Access: Private plans may offer a wider network of healthcare providers, providing more choices for receiving care.
Drawbacks of Private Health Insurance:
- Pre-existing Condition Limitations: Some private plans, especially those not regulated by the ACA, may exclude coverage for pre-existing conditions or impose higher premiums based on health history.
- No Subsidies: Private health insurance plans typically do not offer subsidies or financial assistance, meaning individuals are responsible for paying the full premium and out-of-pocket costs.
- Variable Plan Quality: The quality and comprehensiveness of private health insurance plans can vary widely, and consumers may need to carefully review plan details to ensure adequate coverage.
Conclusion – ACA Vs Private Insurance:
Choosing between ACA health insurance and private health insurance involves evaluating various factors, including coverage needs, financial situation, and preferences. ACA health insurance provides benefits such as comprehensive coverage, financial assistance, and strong consumer protections but may have drawbacks such as potentially high premiums and limited provider networks. Private health insurance offers flexibility, potential cost savings, and broader provider access but may lack subsidies and protections for pre-existing conditions.
Individuals should carefully assess their healthcare needs, budget, and eligibility for financial assistance when making a decision. By understanding the features, benefits, and drawbacks of both ACA and private health insurance, individuals can make informed choices that best meet their healthcare needs and financial goals.
