ACA Obamacare – All You Need To Know In 2024

What is ACA Obamacare?
Are you confused between these two words?
Well, don’t be. We are here to solve your confusion, but for that, you need to read this blog till the end.
For your convenience, we have mentioned everything regarding ACA/Obamacare in the following piece so just go with the flow and remove your confusion.
Happy reading!
The Affordable Care Act (ACA) or Obamacare, as we commonly refer to it, marks one of the most important milestones in the healthcare reform history in the U.S. Put in place by the administration of President Barack Obama in 2010, the ACA was designed and is effective in counting down the barriers within the American healthcare system among others which include access to affordable coverage, insurance market regulations, and healthcare delivery. The ACA has served its purpose for more than a decade already, and undeniably, is the liberating factor of the existing US healthcare system as it has caused a lot of controversies, debates, and transformative changes in the process.
Table of Contents
Obamacare Is the Affordable Care Act (ACA):
The Affordable Care Act (ACA), also known as Obamacare, is a healthcare policy whose main purpose is to increase the number of Americans who can affordably buy insurance. One of the key elements of the ACA includes the “Health Insurance Marketplaces‘, otherwise called “Exchanges”. Health insurance companies offer plans and costs on State & federal Exchanges. With an increasing insured population, productive Rating Health Insurance Exchanges will change health risks in the insurance pool and lead to a reduction in health insurance costs.
The opportunity for the small one is to have adequate medical protection or the possibility of the low-wage earners to have tax allowances or subsidies that help reduce their medical coverage prices and deductibles. The reform policy also opens the door to care for everyone with no prejudice because is prohibited to exclude those who have a pre-existing condition and guarantees that preventive care is to be free of charge.
Many people for barrier reasons, such as first-time health insurance shoppers or those having lost their employer-based insurance are beneficiaries of Obamacare, so the individuals may have a choice of affordable private health insurance. Choosing health insurance is sometimes difficult, but we here have the answers to all your questions including coverages, costs, enrollment, and any changes to Marketplace.
Key Provisions Of ACA Obamacare:
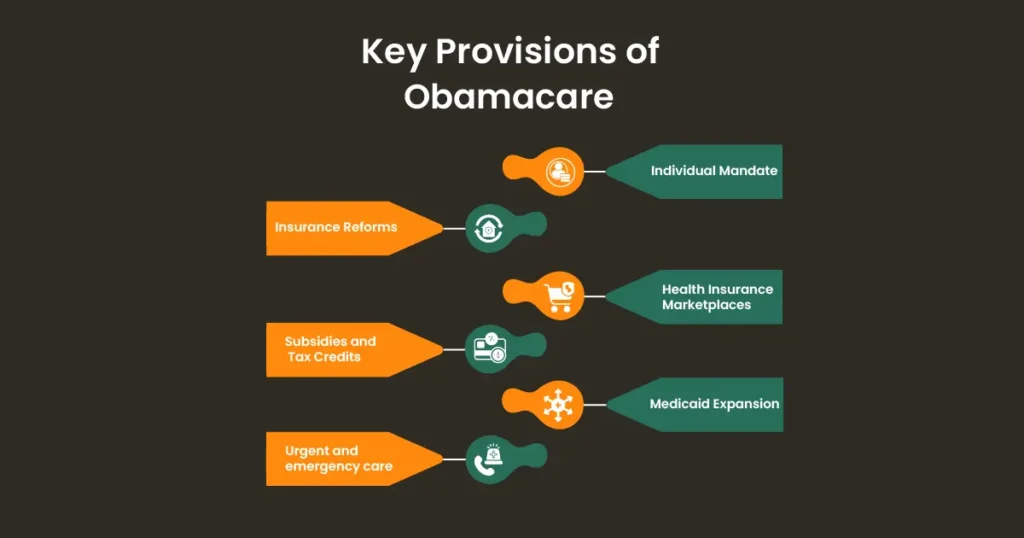
1. Individual Mandate:
At the core of ACA, the individual mandate was the main cornerstone, and it compelled most of the American population to either acquire health insurance coverage or pay a financial penalty. The objective of this measure is to raise the number of insured and share the risk throughout a wider population.
2. Health Insurance Marketplaces:
With the ACA, there came the Health Insurance Marketplaces or the exchanges, platforms where individuals and small businesses were enabled to select or buy insurance plans of their choice. They created an arena for consumers to purchase coverage, which was often underwritten and in this case subsidized, based on individual income level.
3. Medicaid Expansion:
Through ACA, Medicaid security was reinforced to include low-income adult citizens who were eligible because the federal government offered funding to states that decided to expand Medicaid programs. In 2012, the Supreme Court ruled that expansion of Medicaid is a state option which has resulted in inconsistencies regarding eligibility across the country.
4. Insurance Reforms:
Obamacare has added a couple of insurance-related amendments to the market which include customer safeguards and a stable marketplace. Such reforms comprised the prohibition of insurers to reject coverage due to pre-existing conditions, no limits on coverage on one’s entire lifetime or per year, in addition to essential health benefits mandated in all insurance plans.
5. Subsidies and Tax Credits:
To reduce the affordability of health insurance coverage, ACA offers premium subsidies and tax credits to individuals and families who are purchasing insurance through the Health Insurance Marketplaces. These programs ensured that patients’ expenses which are usually borne by them would be lower.
Impact Of ACA Health Insurance:
- Increased Coverage: As a swing of events, ACA has been executed and millions of uninsured citizens got health insurance instead of none. Medicaid’s expansion, resulting in the creation of Health Insurance Markets, induced a noteworthy decrease in the uninsured population.
- Protections for Pre-existing Conditions: One of the many well-liked requirements of the ACA was the ban of insurance providers from rejecting coverage or charging a higher premium due to pre-existing health conditions. Such in permit made it possible for those with chronic conditions or previous medical complications to be provided with complete coverage.
- Young Adult Coverage: ACA made this possible by enabling young adults to stay on their parent’s health insurance until the age of 26. This young adult age group group like students and graduates in the job market was given some time to provide a bridge to obtain coverage as they were transitioning to adulthood.
- Cost Containment Efforts: The health law still has not received a clear decision as to whether or not it was effective in cutting down healthcare costs because various methods, like payoff reforms and healthcare prevention, have met a deep controversy. Even though the opponents of the ACA contend that such provision has not resulted in the slowdown of health care costs, the supporters are advocating that there is still a problem concerning high premiums and high deductibles.
- Health Equity and Access: The ACA set out to deal with the problems of inequality of healthcare and outcomes, which affect mostly the underprivileged population. Yet irrespective of this, there are persisting issues regarding fair access to care, particularly for the poor and those of the communities that are victims of systemic racism and marginalization.
Controversies Regarding ACA Obamacare:
- Political Polarization: ACA has drawn a huge amount of attention becoming a real lightning rod for political discussion and argument which still splits the Republicans and Democrats as to its effectiveness and weaknesses. Attempts to overturn, substitute the ACA, or violate the ACA remained a frequent political problem in the United States, implying the repeal, the replacement, and executive actions.
- Individual Mandate Challenges: The individual mandate generated lots of legal challenges, culminating in a 2012 judgment from the Supreme Court that it nevertheless conformed with the Constitution as a form of tax. While the law still imposes a penalty on those who do not choose health coverage, in 2017 this penalty was effectively nullified by tax reform statutes causing concern over the long-term sustainability of the mandate.
- Medicaid Expansion Disparities: This Supreme Court judgment granting states the option to expand Medicaid has led to a disparate coverage system in the country. Therefore, many poor live in non-expanded states and have no health insurance which only demonstrates the degree of political intervention goes through in applying the health care system.
Future Outlook:
As the healthcare arena undergoes constant dynamism, there is a lot of possibility of the ACA matters remaining uncertain. Despite the promising approach of the Biden administration, which supports broadening and strengthening the ACA, whether this could take place or not will be a result of their successful negotiations with the legislature, opponents, and further research on how affordability, accessibility, and quality of the healthcare can be improved. Though it remains to be seen, whether the ACA will survive or not, it did not leave without making a spectacular leap in the USA healthcare that will be remembered for its shape of healthcare in the future.
Can You Be Denied Obamacare?
If you are eligible for Obamacare, it can be reassuring to know that you cannot be denied coverage under the Affordable Care Act. This means that if you are a lawful resident of the United States and are not currently incarcerated or covered by Medicare, you have the opportunity to enroll in an ACA insurance plan. However, it is important to note that depending on your income and other factors, your plan may not qualify for subsidies.
Additionally, if you attempt to sign up outside of the annual open enrollment period, your application may be denied. To ensure that you can enroll in a plan for 2023 coverage, it is important to know that the open enrollment deadline is January 15, 2023, for most people. If you are looking to have your coverage begin on January 1, 2023, then the deadline to enroll is December 15, 2022, in most states.
How Do I Enroll in Obamacare?
Hospitals and clinics distribute plans on a single marketplace and for a single time of the year, which is usually the Open Enrollment Period (OEP). The application for the OEP is open from Nov 1 to Dec 15. New plans purchased during this period will be effective as of Jan. 1 of the next year. If you are considering re-enroll, it can also work for you.
Exceptions, known as Qualified Life Events (QLEs), will make you eligible for a Special Enrollment Period, including Exceptions, known as Qualified Life Events (QLEs), will make you eligible for a Special Enrollment Period, including:
- Marriage.
- Acquiring or finalizing a child through birth or adoption.
- Permanent residency and any option you had before are no longer valid.
- Income rise or loss of employment.
- Having no health insurance (involuntary).
Where To Enroll:
Whether you are seeking to start coverage under the ACA in your name or you wish to guide somebody else through the enrollment process during the period of open enrollment, you can do so through different methods.
Take the step online to enroll, and that is, apply on The Marketplace at www.Healthcare.gov or enroll by phone through The Marketplace call center at 855-318-2596.
Conclusion – ACA Obamacare:
Obamacare, otherwise known as the Affordable Care Act, was a remarkable attempt to reform the healthcare industry in the United States. The main goal of this legislation was to enlarge the number of citizens with healthcare coverage that was cheaper and extended to millions of Americans who could not get it or had it pulled out because they had pre-existing conditions. The ACA brought many changes to medical institutions, including new restrictions and regulations on insurance companies, the creation of the state and federal marketplaces, as well as an extension of the coverage of Medicaid.
Even though the ACA ensured people of whichever background have equal opportunities for accessing healthcare finally, the Act was found to have many flaws and shortcomings. Some drummed up resistance, saying that was cost-prohibitive, whereas others criticized it because it did not accomplish enough in covering people who needed it. Moreover, the ACA remains a subject of debate, particularly regarding the impacts it has brought in terms of the economy, healthcare costs, and the overall quality of healthcare.
With all its flaws, there is no doubt that the Affordable Care Act (ACA) has a place in the healthcare policy of the United States. The future of American healthcare will follow this leading act and its legacy for a long time. As the healthcare industry is rocked by changes every day, the ACA will certainly be instrumental in determining the programs, rules, as well as laws to be followed by all medical institutions.
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS:
Q: What are Obamacare’s benefits?
A set of 10 categories of services health insurance plans must cover under the Affordable Care Act. These include doctors’ services, inpatient and outpatient hospital care, prescription drug coverage, pregnancy and childbirth, mental health services, and more.
Q: Is Obamacare only for US citizens?
To be eligible to enroll in health coverage through the Marketplace, you must: Live in the United States (U.S). Be a U.S. citizen or national, or be lawfully present non-citizen in the U.S. Learn about eligible immigration statuses.
Q: How much does Obamacare cost America?
Obamacare costs an average of $584 per month for a 40-year-old with a Silver plan. Your age affects your monthly rates. A 20-year-old pays an average of $443 per month for a Silver plan, while a 60-year-old pays an average of $1,240 per month, before subsidies.
